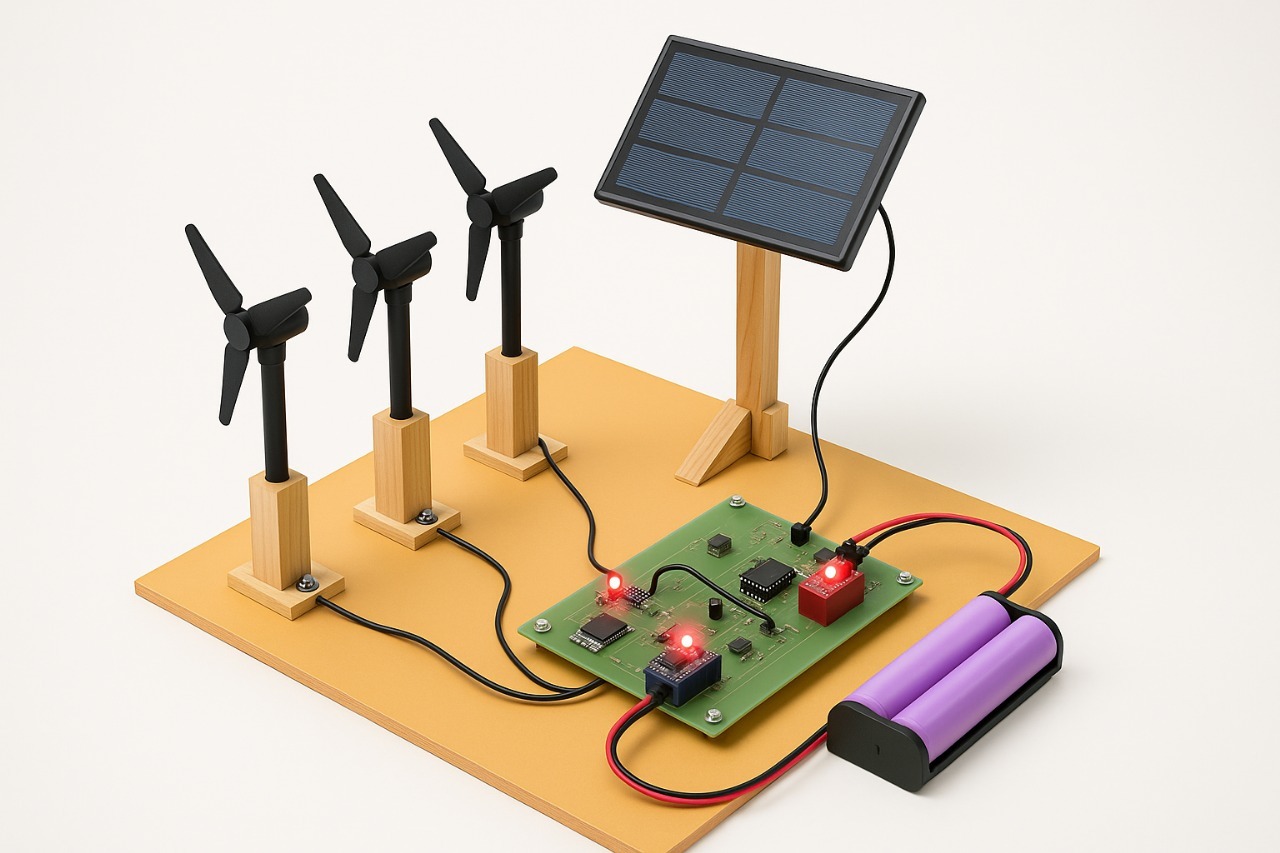
“Dwel Power Generation”
This paper discusses a novel method of power generation by utilizing the weight of dwellings (houses or buildings) and gravitational force.
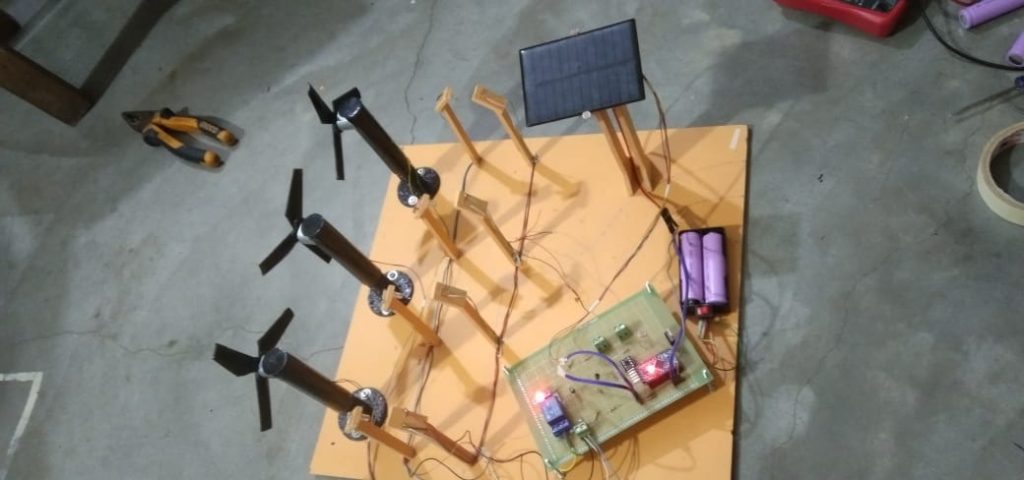


Ladyship it daughter securing procured or am moreover mr. Put sir she exercise vicinity cheerful wondered. Continual say suspicion provision you neglected sir curiosity unwilling. Simplicity end themselves increasing led day sympathize yet. General windows effects not are drawing man garrets. Common indeed garden you his ladies out yet. Preference imprudence contrasted.
Working Principle:
-
A house or structure is mounted on a platform connected to a mechanical system.
-
The weight of the house applies a constant downward force.
-
This force is transferred through gear mechanisms and pulleys.
-
The mechanical energy is converted into rotational energy, which drives a generator to produce electricity.
Block Diagram
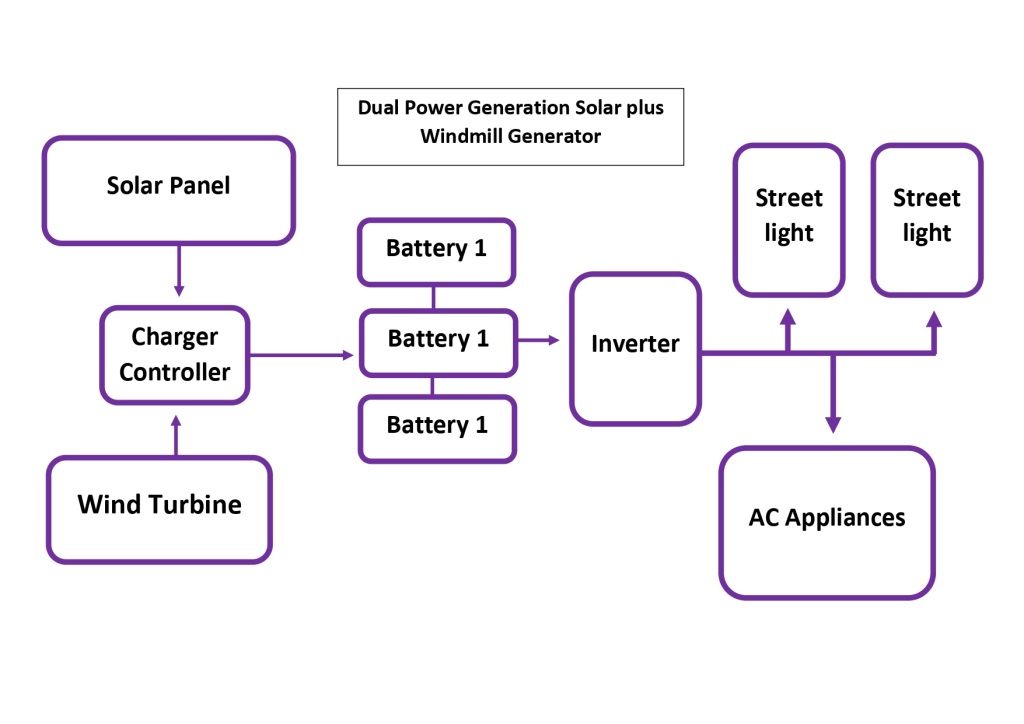
Technical Components:
-
Gear systems (rack and pinion)
-
Pulley and rope mechanisms
-
Rotating shaft connected to a generator
-
Load-bearing platform
-
Storage system for electrical energy (like batteries)
Environmental Significance:
-
Uses no fossil fuel, no solar radiation, and no wind dependency.
-
Provides a sustainable, environment-friendly alternative power source.
-
Reduces CO₂ emissions significantly.
-
Utilizes constant, reliable gravitational force.
Advantages:
-
Continuous and consistent power generation.
-
Low maintenance after installation.
-
Space-efficient, as it uses existing buildings.
-
Environmentally safe and quiet operation.
Limitations:
-
Initial setup may be complex and costly.
-
Requires precise structural balancing.
-
Not yet widely tested in large-scale real-world environments.
-
Efficiency needs further optimization and testing.
Additional Highlights:
-
The paper includes diagrams showing mechanical arrangements.
-
Describes the theoretical background, force calculations, and energy conversion formulas.
-
Includes comparisons with other renewable energy sources.
-
Contains experimental designs and test models.